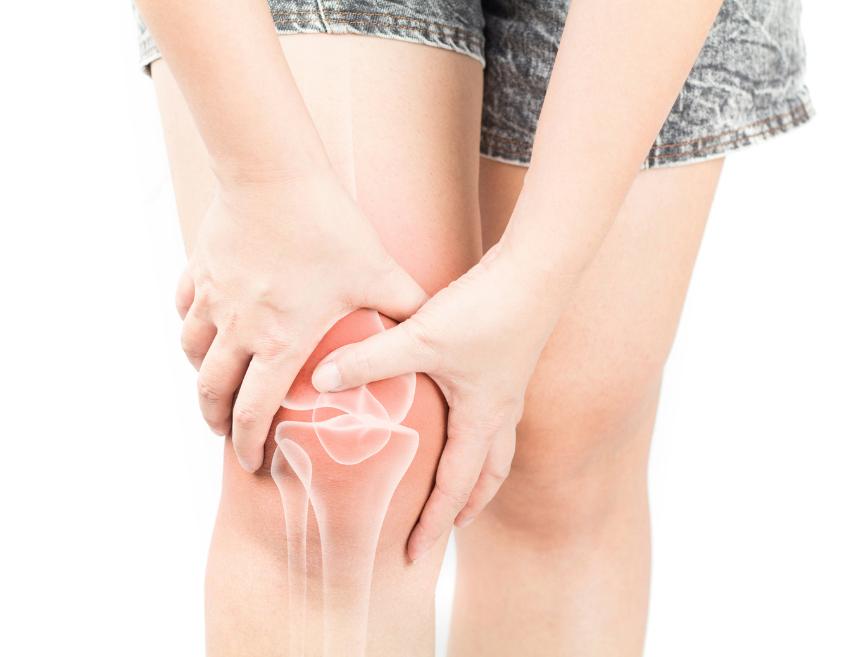
Osteoporosis: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a silent disease that affects the density and quality of bones, making them more fragile and increasing the risk of fractures. This condition occurs when bone formation doesn’t keep up with its natural resorption, leading to progressive bone loss. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications, such as spontaneous fractures and mobility limitations.
Osteoporosis is more common in postmenopausal women due to the reduction in estrogen levels, but it can also affect men, particularly as they age. Other factors, such as a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and chronic diseases, can accelerate bone loss. Furthermore, individuals with a family history of the disease should have closer medical monitoring to assess bone density regularly.
Osteoporosis can significantly impact quality of life by affecting the ability to perform daily activities and reducing people’s independence. Prevention and appropriate treatment are essential to prevent disease progression and ensure greater well-being.
Symptoms of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is often asymptomatic until a fracture occurs. However, some signs may indicate the presence of the disease:
- Height loss over time due to vertebral weakening.
- Curved posture, which can result in chronic back pain.
- Back pain caused by microfractures in the vertebrae that may go unnoticed.
- Frequent fractures, especially in the wrists, spine, and hips, even after low-impact falls.
If osteoporosis is suspected, tests such as a bone mineral density scan help assess bone density and fracture risk. Additionally, it is recommended that individuals over 50 have regular tests to monitor bone health and detect possible bone density loss before fractures occur.
Causes and Risk Factors
Osteoporosis can be caused by several factors, including:
- Natural aging of the body, leading to reduced bone regeneration.
- Calcium and vitamin D deficiency, essential for bone mineralization.
- Lack of physical exercise, which reduces stimulation for bone strengthening.
- Excessive alcohol and tobacco use, which impair nutrient absorption.
- Genetic predisposition, with a family history of the disease.
- Prolonged use of corticosteroids, which interfere with bone metabolism.
- Diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, and hormonal disorders that can compromise bone health.
Postmenopausal women have an increased risk due to the drop in estrogen levels, a hormone essential for maintaining bone density. For this group, preventive measures are even more important to avoid future complications.
Treatment for Osteoporosis
The treatment of osteoporosis aims to slow bone loss and reduce fracture risk. Options include:
- Medications such as bisphosphonates, denosumab, and teriparatide, which work to preserve and form bones.
- Calcium and vitamin D supplementation to help maintain bone health.
- Lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet and regular physical exercise.
- Hormone therapies for postmenopausal women, helping to minimize accelerated bone loss.
Medical supervision is essential to determine the best treatment plan for each case. Adhering to the treatment plan is crucial to achieving good results and reducing the risk of future fractures.
How to Prevent Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis prevention involves a healthy lifestyle. Some measures include:
- Moderate sun exposure to stimulate vitamin D production, essential for calcium absorption.
- Weight-bearing and impact exercises, such as walking, running, and weight training, to strengthen bones.
- Avoiding tobacco and reducing alcohol consumption, which accelerate bone loss.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to prevent joint and bone overload.
- Adequate protein intake, which is essential for maintaining bone and muscle structure.
Additionally, practices such as physiotherapy may be recommended to strengthen muscles and improve posture, reducing the risk of falls and fractures associated with osteoporosis.
Exercises for Osteoporosis Without Leaving Home
Physical exercise is essential for strengthening bones and preventing falls, especially as we age. Regular physical activities, such as weight training and impact exercises, help increase bone density and prevent osteoporosis, as demonstrated by scientific studies. One example is a systematic review indicating that high-intensity physical activities are effective in preventing osteoporosis.
Additionally, weight training strengthens both bones and muscles, which is crucial for preventing falls. It is important to adopt an active lifestyle, not just react when health issues arise, as physical activity improves quality of life and overall well-being.
Starting with simple exercises and professional guidance can be an excellent way to strengthen bones and prevent falls.
Physical exercise is essential for strengthening bones and preventing falls. Some safe options to do at home include:
Marching in place: Helps maintain mobility, strengthen legs, and improve balance. For a more complete and safe workout, using an exercise peddler can be an excellent option to strengthen both arms and legs.
Heel raises: Strengthen the bones in the feet and ankles, reducing the risk of fractures. For a more comfortable and accessible alternative, an electric peddler can help maintain mobility and stimulate blood circulation.
Pilates circle: Helps with flexibility and muscle strengthening, improving posture and preventing falls. Ideal for those who want to practice low-impact exercises at home.
Elastic band exercises: Improve muscle strength without excessive strain, ideal for beginners.
Other exercises such as stretching and balance training can be incorporated into the routine to improve motor coordination and reduce the risk of falls, which are a leading cause of fractures in people with osteoporosis.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis is a disease that can compromise quality of life, but it can be prevented and controlled with an adequate lifestyle. Maintaining a calcium-rich diet, practicing regular exercise, and using equipment such as peddlers and Pilates circles are effective strategies to strengthen bones and prevent complications. Additionally, regular medical check-ups and bone density tests are essential to diagnose the disease early and avoid serious consequences.
Investing in osteoporosis prevention from an early age can ensure a healthier and more active old age. Small changes in daily life can make all the difference in maintaining bone health and avoiding future complications. If you want to invest in your bone health, explore the options at Loja Ortopédica and find the best products for your needs.






No Comments