Shoulder Tendonitis: Symptoms, Treatments, and Prevention Tips
What is Shoulder Tendonitis?
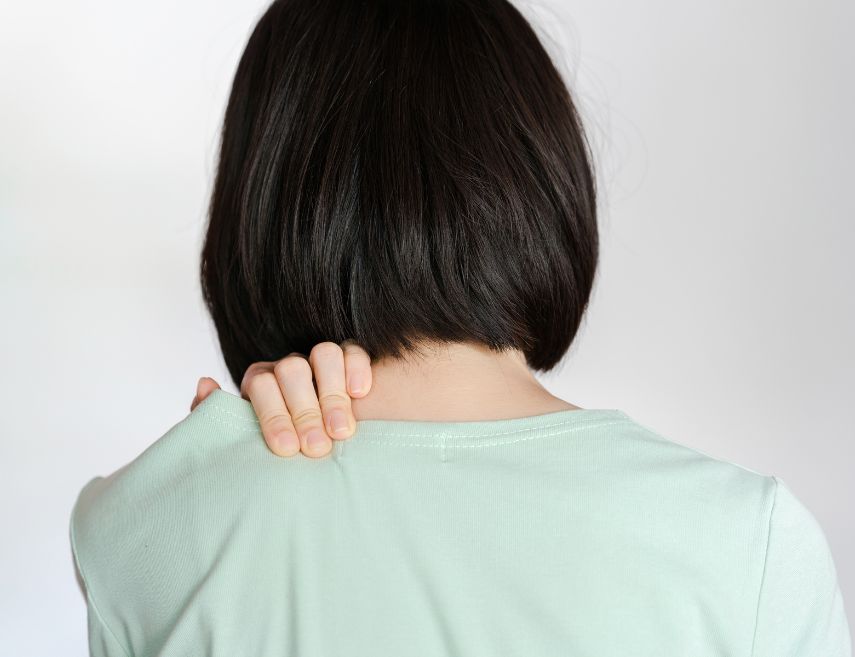
Shoulder tendonitis is an inflammation of the tendons surrounding the shoulder joint. This condition is often caused by repetitive movements, muscle overuse, natural aging of tissues, and, in some cases, systemic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Tendonitis primarily affects the rotator cuff, a structure composed of muscles and tendons responsible for shoulder mobility and stability. Over time, continuous inflammation can lead to chronic pain, loss of strength, and limited movement. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential to minimize symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening.
How to Identify Shoulder Tendonitis? Key Symptoms and Warning Signs
The symptoms of shoulder tendonitis can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of inflammation and the duration of the problem. Recognizing warning signs early is crucial to ensure a timely diagnosis and prevent the condition from becoming chronic. The main symptoms include:
- Pain when raising the arm: Pain when lifting the arm, especially when reaching for objects overhead, is one of the first signs of shoulder tendonitis.
- Stiffness: A feeling of stiffness and difficulty moving the shoulder. In some cases, this stiffness can make simple tasks, such as dressing, challenging.
- Swelling and tenderness: The affected area may appear swollen and be sensitive to touch.
- Night pain: Pain may worsen at night, especially when lying on the affected side, often interfering with sleep.
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional if you notice these symptoms, as early diagnosis is critical to preventing the development of chronic shoulder tendonitis. Studies show that early treatment increases effectiveness and reduces the risk of complications.
Types of Shoulder Tendonitis
There are different types of shoulder tendonitis, and treatment may vary depending on the specific type. The two most common types are:
1. Calcific Tendonitis of the Shoulder
Calcific tendonitis occurs when calcium deposits build up in the shoulder tendons, causing inflammation and severe pain. This type of tendonitis is more common in people aged 30 to 50 and usually affects the supraspinatus tendon. The pain can be very intense, making simple movements and daily life difficult.
Treatment for calcific tendonitis may include physical therapy to strengthen the joint, medications to relieve pain, and, in severe cases, surgery to remove calcium deposits. Studies indicate that conservative treatment, including specific exercises and ice application, can significantly reduce pain and the size of the deposits.
2. Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder. Tendonitis in this area often results from repetitive movements or poor posture. This type of tendonitis is common among athletes and people who work with their arms raised.
To treat rotator cuff tendonitis, rest is essential, followed by physical therapy to strengthen the muscles and improve mobility. In some cases, a doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medications to relieve pain.
How to Treat Shoulder Tendonitis? Main Treatment Methods
Treating shoulder tendonitis is essential to relieve symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening. Several approaches can be used alone or in combination, depending on the case’s severity and medical advice. Below are the main options:
1. Rest and Habit Modification
Resting the shoulder is crucial to reducing inflammation and allowing tissues to recover. Avoiding activities that cause pain, such as lifting weights or performing repetitive movements, can help speed up recovery. Additionally, maintaining proper posture and avoiding positions that strain the shoulder are important practices to prevent the recurrence of tendonitis.
2. Hot and Cold Therapy
Alternating between cold and heat is an effective technique to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Cold compresses help decrease swelling, while heat improves circulation and alleviates muscle stiffness. For optimal results, we recommend:

Sport Gel 100ml Rowo
Use Sport Gel 100ml Rowo after physical activities or when experiencing intense pain, as it helps reduce swelling.

Flexi Forte Hot Gel with Harpago Rowo
Alternate the sport gel with Flexi Forte Hot Gel with Harpago Rowo, especially before performing stretching exercises or physical therapy, to promote circulation and relax muscles.
3. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is one of the most effective options for treating shoulder tendonitis. Through specific exercises, physical therapy helps strengthen the muscles around the shoulder, improving stability and preventing future injuries. A physical therapist can recommend a combination of strengthening and stretching exercises tailored to your condition.
Studies suggest that regular physical therapy programs can significantly reduce tendonitis symptoms and improve patients’ quality of life.
4. Use of Shoulder Supports
Shoulder supports are essential to stabilize the joint and reduce pain during movement. These supports can be especially useful for those who need to continue working or performing activities with the affected shoulder. Recommended products include:

Elastic Functional Shoulder Support
A model with 3D elastics, perfect for daily use, providing comfort without causing discomfort.
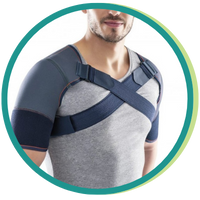
Bilateral Neoprene Shoulder Support
Provides compression and pain relief in both shoulders if needed.
Neoprene shoulder supports are ideal for preventing injuries during sports and aiding recovery. This material is particularly recommended for physical activities or warming the shoulder area on colder days, as it helps relax the muscles.
There are models available for the left, right, or both shoulders, allowing you to choose the most suitable for your needs.
5. Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Anti-inflammatory drugs can be prescribed to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. However, these medications should be used under medical supervision, as prolonged use may cause side effects.
6. Invasive Procedures
In severe cases, the doctor may recommend invasive procedures such as corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation or surgery to remove calcium deposits in calcific tendonitis. These options are considered only when conservative treatments do not yield satisfactory results.
Tips for Preventing Shoulder Tendonitis
Preventing shoulder tendonitis is possible with a few daily practices that help maintain joint health and avoid tendon inflammation. To reduce the risk of developing this condition, consider the following tips:
- Avoid repetitive movements: Whenever possible, minimize repetitive motions involving the shoulders. In jobs requiring constant arm use, take regular breaks.
- Muscle strengthening: Keeping shoulder muscles strong is essential for providing support and stability to the joint. Perform exercises that strengthen the rotator cuff under professional guidance to prevent tendonitis.
- Regular stretching: Daily stretching helps maintain flexibility in muscles and tendons, reducing stiffness and the risk of injury.
- Practice good posture: Avoid improper posture during work and physical activities to prevent shoulder strain and reduce the risk of tendonitis.
Studies show that a routine of stretching and muscle strengthening can reduce tendonitis incidence by up to 50% in populations at high risk of developing the condition.
Shoulder tendonitis is a condition that can limit mobility and affect quality of life. With proper diagnosis and a treatment plan that includes rest, physical therapy, and the use of supports and gels, it is possible to manage symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening. Adopting preventive practices and following specific treatments can make a significant difference, ensuring greater mobility, pain relief, and a more active and healthy life.




No Comments